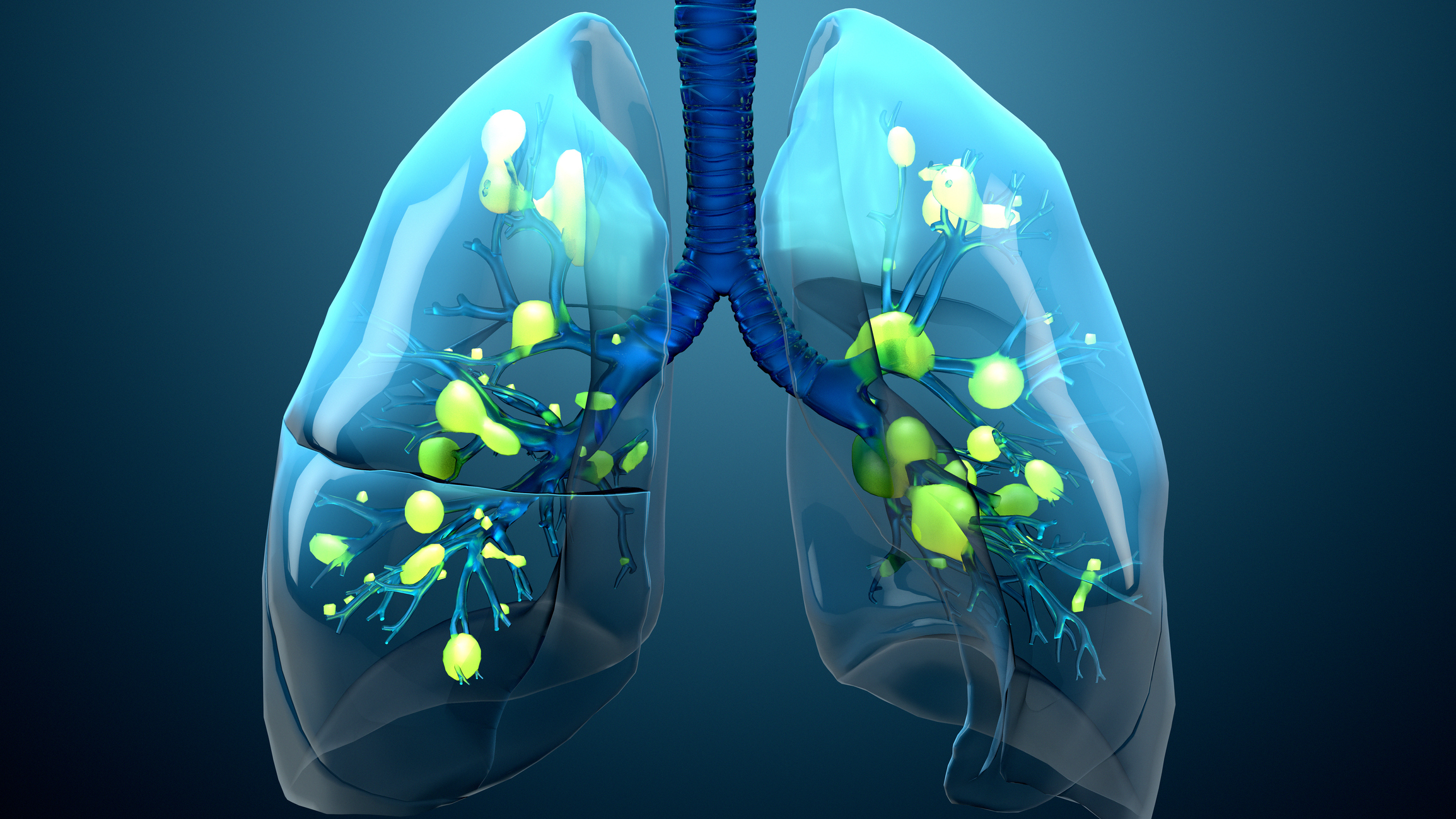
Inhalation of air pollutants, such as particulate matter (PM), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and sulfur dioxide (SO2), can lead to respiratory problems. This includes aggravated asthma, chronic bronchitis, and decreased lung function.
Air pollution is a significant environmental concern that arises from the release of various pollutants into the Earth's atmosphere. These pollutants can have wide-ranging effects and impacts on human health, ecosystems, and the overall quality of the air we breathe. The consequences of air pollution are diverse and can manifest at different levels, from local to global scales
Here, we delve into the detailed effects and impacts of air pollution:
Inhalation of air pollutants, such as particulate matter (PM), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and sulfur dioxide (SO2), can lead to respiratory problems. This includes aggravated asthma, chronic bronchitis, and decreased lung function.

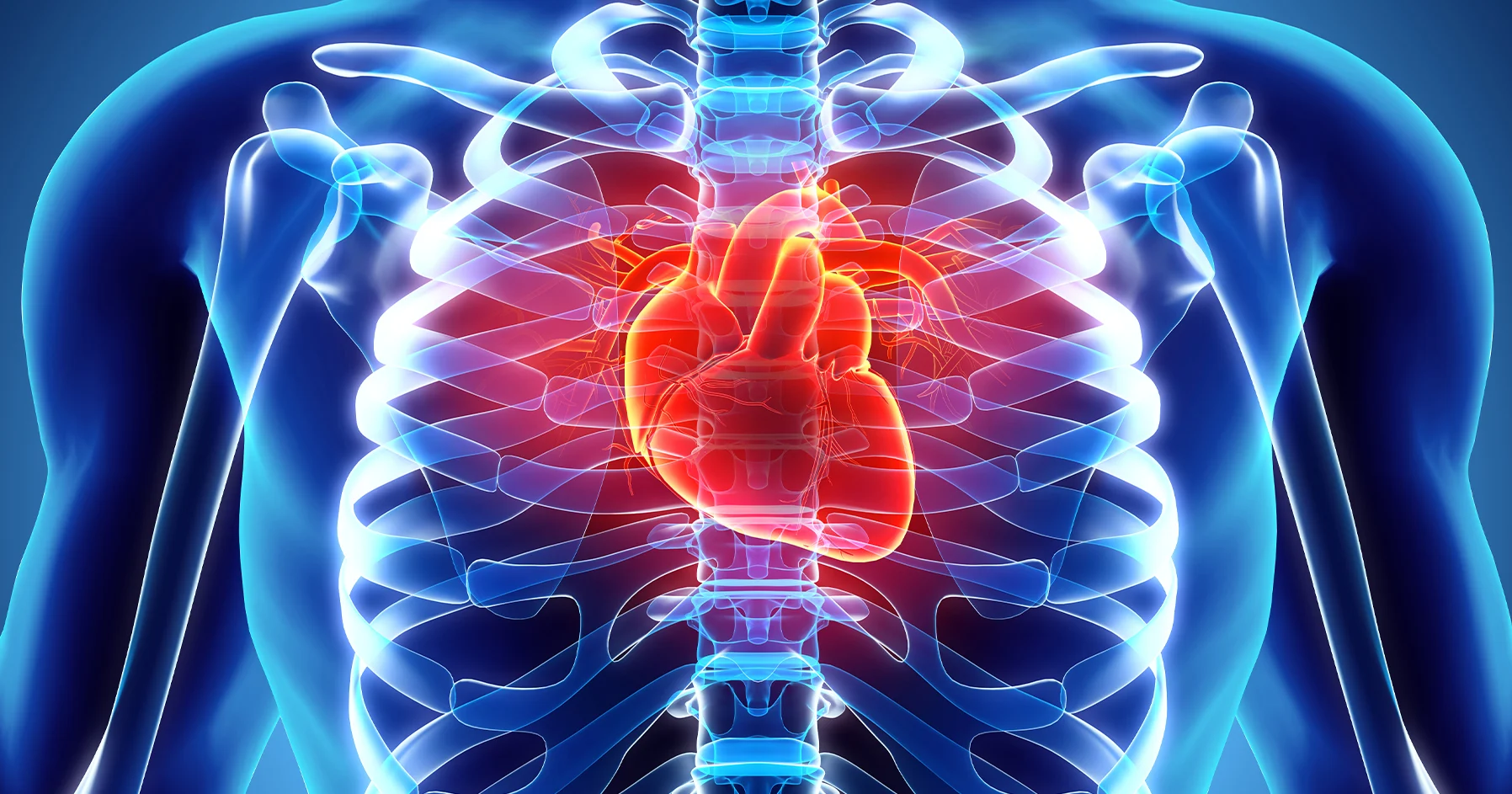
Long-term exposure to air pollution has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes.
Inhalation of air pollutants, such as particulate matter (PM), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and sulfur dioxide (SO2), can lead to respiratory problems. This includes aggravated asthma, chronic bronchitis, and decreased lung function.
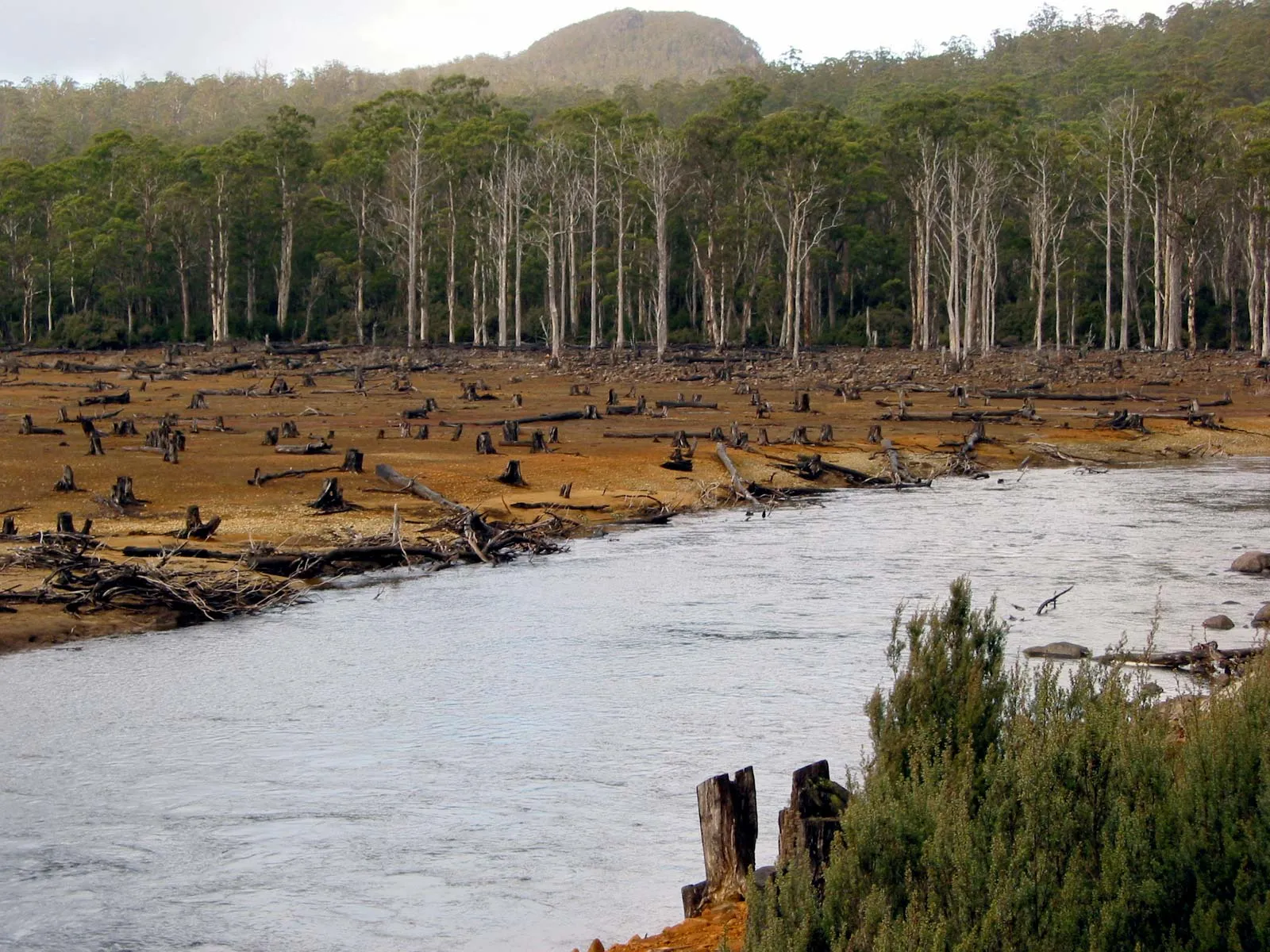
Air pollutants can harm plants, animals, and aquatic ecosystems. Acid rain, resulting from the deposition of sulfur and nitrogen compounds, damages soil, water bodies, and vegetation


The decline in air quality contributes to habitat degradation and loss, impacting the biodiversity of various ecosystems. Sensitive species may face population declines or extinction
Air pollutants can harm plants, animals, and aquatic ecosystems. Acid rain, resulting from the deposition of sulfur and nitrogen compounds, damages soil, water bodies, and vegetation


Air pollution can influence weather patterns, leading to changes in precipitation and temperature. This can affect ecosystems and agricultural productivity.
Particulate matter and ground-level ozone contribute to the formation of haze and smog, reducing visibility in urban areas. This not only affects aesthetic values but also poses transportation and safety hazards

The health effects of air pollution result in increased healthcare expenditures. Treating respiratory and cardiovascular diseases places a burden on healthcare systems and can lead to productivity losses.

Ozone and other pollutants can harm crops, affecting agricultural yields and food production. This has economic ramifications for both farmers and consumers
Poor air quality diminishes the overall quality of life in affected areas. Residents may experience discomfort, stress, and limitations on outdoor activities
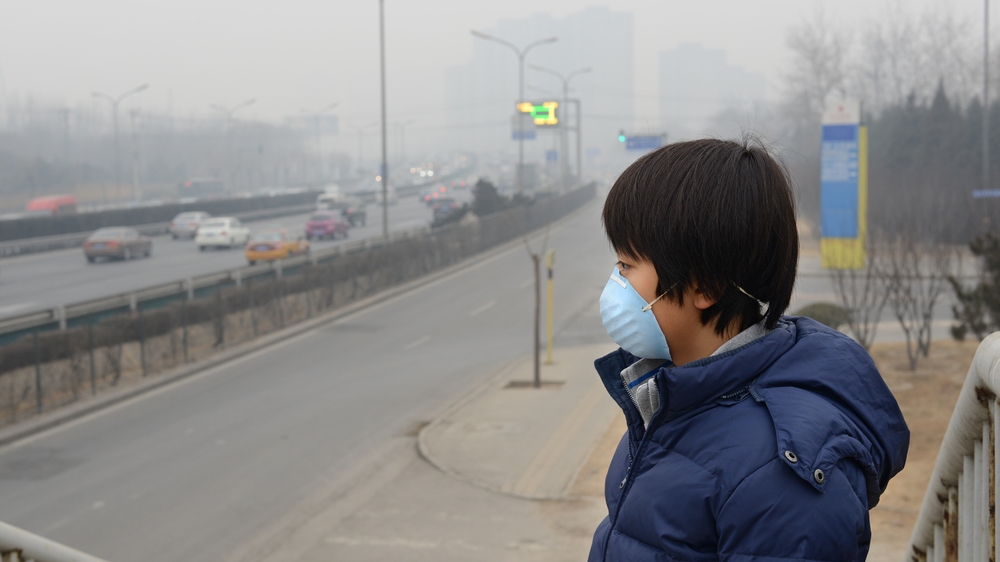
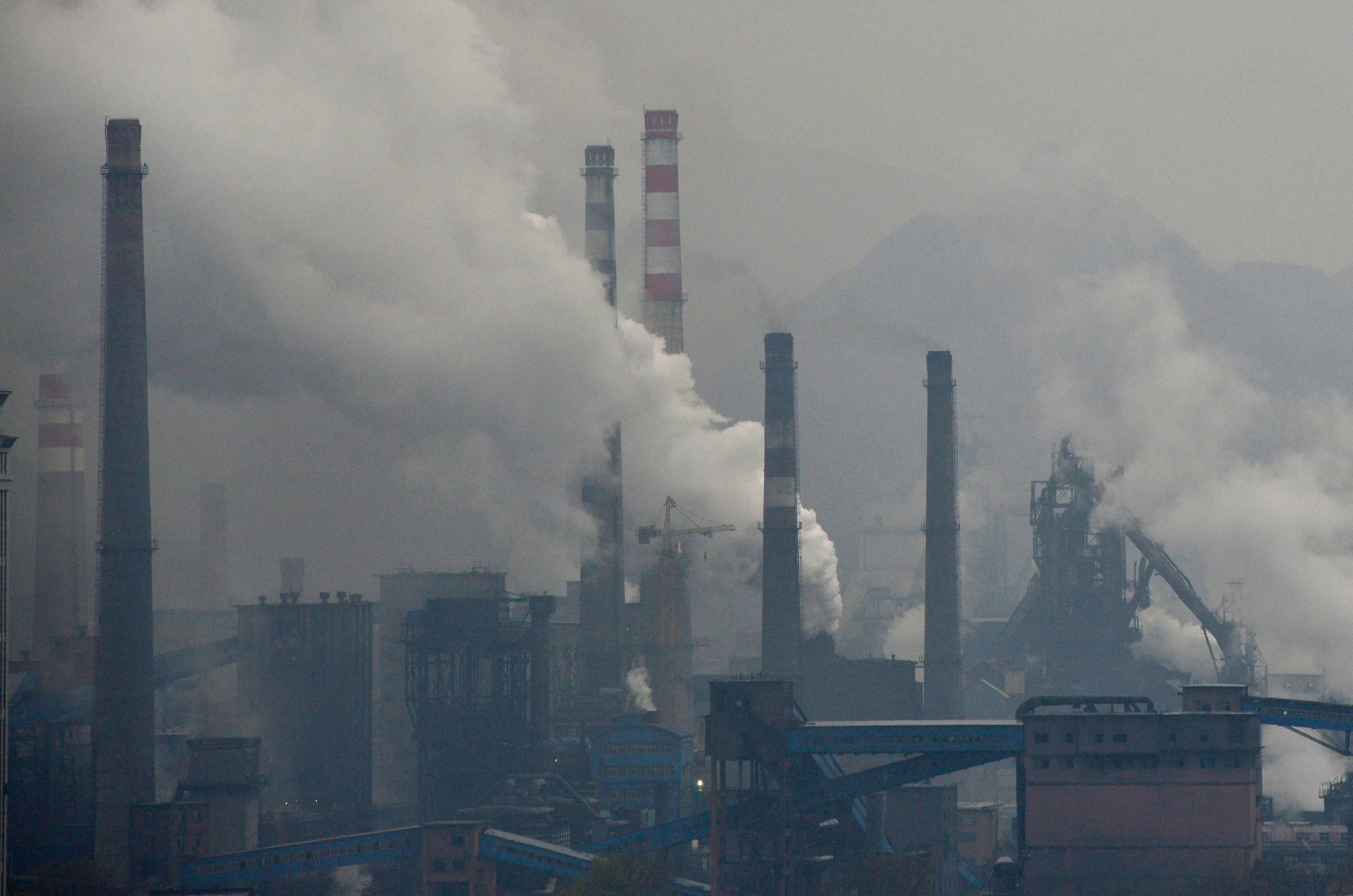


Vulnerable populations, such as low-income communities, often bear a disproportionate burden of air pollution, exacerbating existing social inequalities
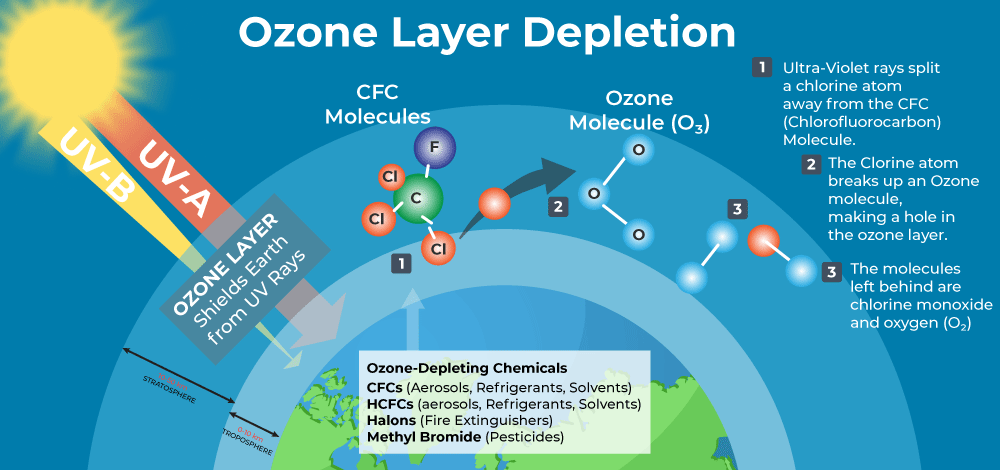
Certain air pollutants, such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), contribute to the depletion of the ozone layer in the stratosphere. This poses risks to human health and ecosystems by increasing exposure to harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation
You can see the images by clicking the button below to see how air pollution effects us